Spanish Case study
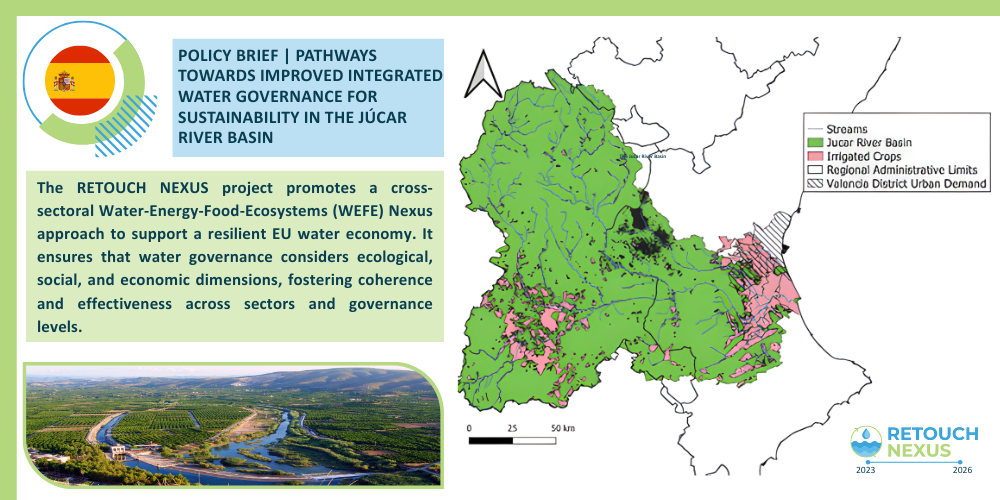
Júcar River Basin
The Júcar river basin, located in the Mediterranean basin of eastern Spain, is a vital water resource system operating under a delicate balance.
Case Study Overview
Discover Valencia's Challenges
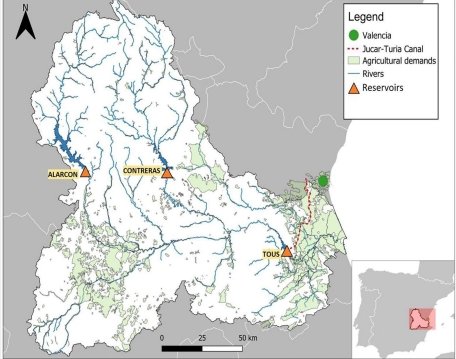
The Júcar River is the main water source for Valencia, Spain’s third-largest municipality, facing frequent and severe droughts due to water scarcity, irregular hydrology, and over-exploitation of groundwater. This situation is worsened by global climatic changes and political disputes between Castilla-La Mancha and Valencia. Innovative solutions are needed for sustainable water management to mitigate drought impacts. Efficient water governance and economic tools are crucial to balancing water use with energy production, agriculture, and environmental sustainability, aligning with the Water Framework Directive (WFD) goals.
Our Methodology
Traditional Approaches vs. Innovative Solutions
Historically, Spain has addressed water scarcity by increasing available resources. However, this approach is nearly exhausted in the Júcar River basin, where the use of non-conventional water resources is often prohibitively expensive, especially in the context of rising energy prices.
The Júcar river basin’s water governance is characterized by a centralized planning approach led by the Júcar River Basin Authority (CHJ). This centralization ensures that water resources are managed efficiently and sustainably. Additionally, water management is collaboratively handled by the Comisión de Desembalse, which includes representatives from CHJ, water users, and government officials. This collaborative effort ensures that diverse perspectives are considered in decision-making processes. Local indicators used for monitoring water governance include the existence and implementation level of water laws, the presence of a central agency with water-related responsibilities, mechanisms for reviewing responsibilities, integrated water resource management strategies, and institutions managing hydrographic resources.
To achieve sustainable water use, innovative water governance schemes and economic instruments are needed to balance demand with availability, support energy and agriculture, ensure environmental protection, and advance towards the Water Framework Directive (WFD) goals.
Our methodology develops innovative solutions for sustainable water governance within the WEFE Nexus framework, including climate-adjusted economic instruments, business models for the EU water economy, and climate change adaptation measures for long-term resilience.
Our Local Engagement Activites
Engaging Stakeholders to Address Water-Related Issues
RETOUCH NEXUS Presented at the International Workshop WEARE-EAARN-FICOTUR in Córdoba
RETOUCH NEXUS was represented at the International Workshop WEARE-EAARN-FICOTUR: Establishing Networks, held on 22–23 January 2026 in Córdoba, Spain, within the session “Instruments and Policies…
New Policy Brief: Pathways Towards Improved Integrated Water Governance in the Júcar River Basin
Integrated Water Governance in the Júcar River Basin: Turning Scarcity into Resilience The Júcar River Basin, Valencia's main water source,…
Valencia Hosts Key Workshop on Climate Change Adaptation in the Júcar River Basin
Experts, policymakers, and environmental stakeholders gathered on April 4th at the IIAMA-UPV headquarters in Valencia for a workshop titled “Adapting…
Establishing a baseline to characterise each RETOUCH NEXUS case study
Last September, our project completed two tasks aimed at exploring water governance models, institutional frameworks and economic, financial and commercial…