Casestudie Duits
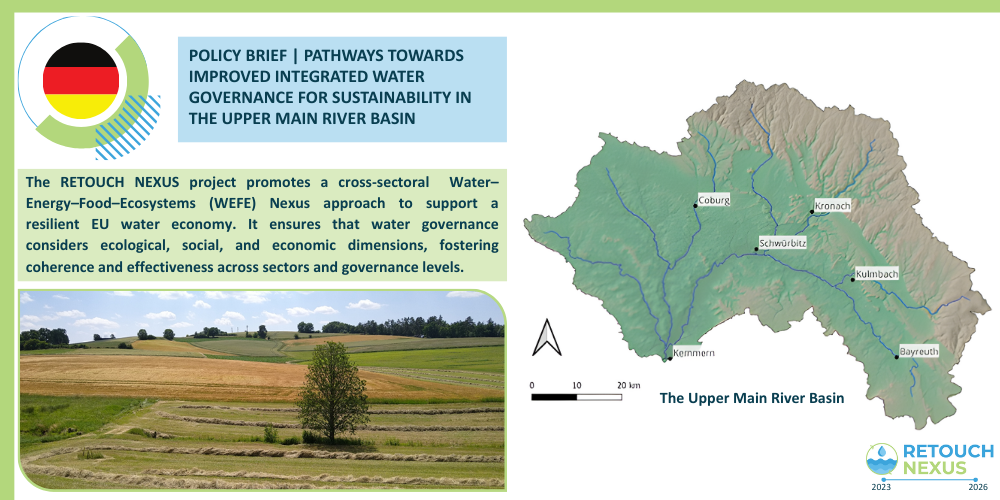
Ober Main in Noord-Beieren
Explore how our team is strengthening stakeholder collaboration in the highly interconnected WEFE system of the Upper Main study area.
Overzicht casestudy
Ontdek de uitdagingen van Duitsland
In Bavaria, a traditional top-down approach to water management is used, but Germany aims to increase digitization in its authorities. Online engagement tools and citizen science could modernize water governance. However, communication and knowledge remain fragmented among governing institutions and water users in the Upper Main region. Frequent hydrological extremes, such as floods and droughts, have heightened tensions among stakeholders, particularly affecting agricultural production due to water scarcity.
There is an urgent need to resolve these tensions while ensuring environmental sustainability. Expanding the analysis to include the entire Main catchment area could involve additional water authorities and federal states.
Our Methodology & Expected Results
Harmoniseren van watergebruik en milieubalans
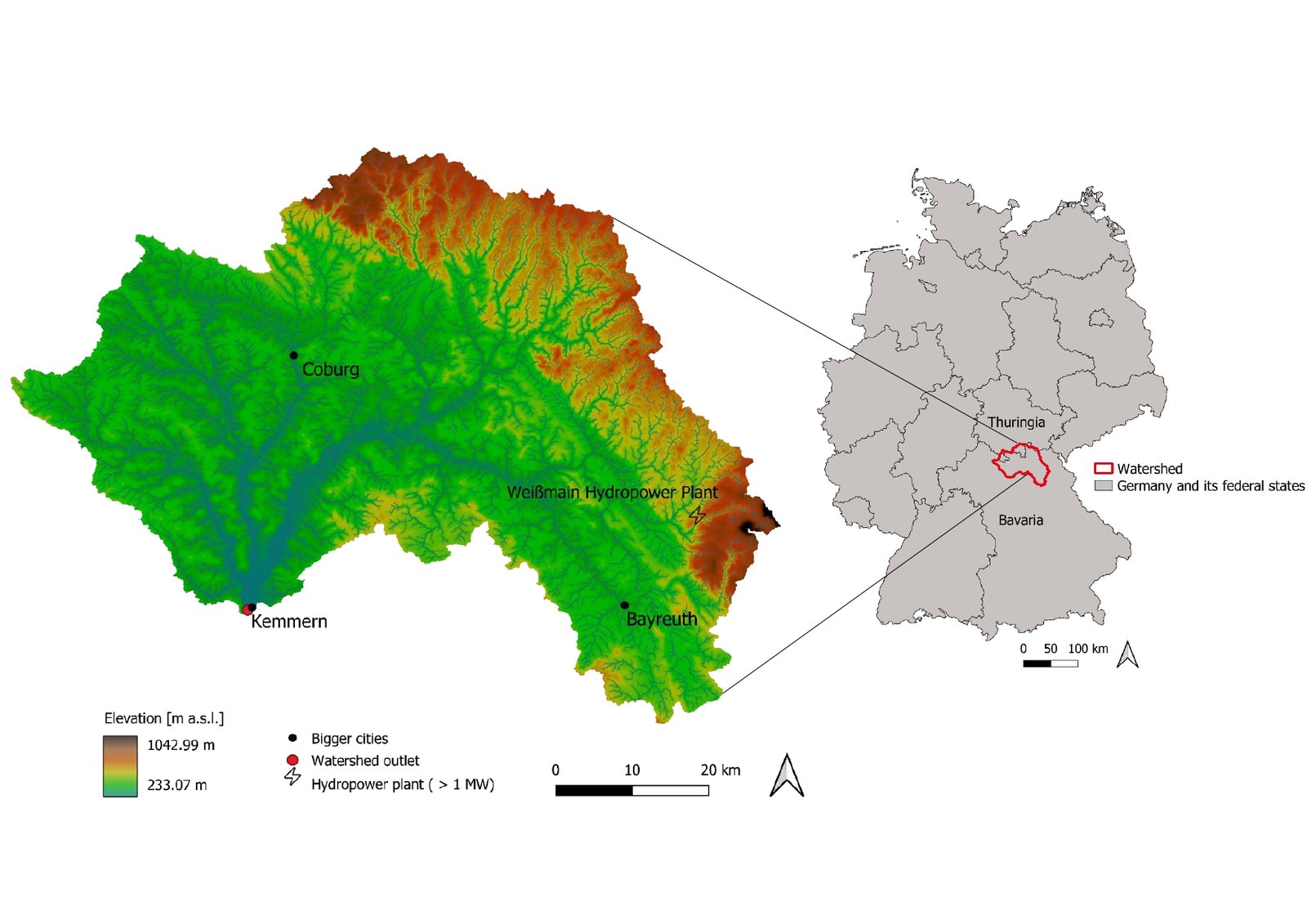
Het bovenste hoofdstroomgebied ligt in het noordelijke deel van Beieren in Duitsland (zie figuur 1). Het stroomgebied heeft een oppervlakte van 4.646 km2 (Gauge Kemmern) (Schaffhauser, T., 2017) en wordt gekenmerkt door een oost-westhelling die de hoogste hoogten bereikt met 1042,99 m boven zeeniveau in het Fichtelgebergte. 75% van het gebied ligt echter in lager gelegen gebieden (Barth et al., 2004). Gronden met een lage opslagcapaciteit overheersen (Schaffhauser, T., 2017) en het meest voorkomende bodemtype is bruine aarde (Barth, et al., 2004).
Het grootste deel van het stroomgebied wordt gebruikt voor land- en bosbouw met een aandeel van respectievelijk 47,2% en 43,2%, terwijl 8,0% van het gebied is afgedicht. Het grootste deel van het landbouwgebied (60,3%) wordt niet geïrrigeerd. De bovenste hoofdleiding heeft twee bronnen (witte en rode hoofdleiding) en verschillende zijrivieren (Schaffhauser, T., 2017). Naast meer dan 350 mini-waterkrachtcentrales is er één waterkrachtcentrale met een capaciteit > 1MW (LfU,2023).
Most of the public water supply is provided by groundwater (64.0 %), followed by spring water (16.1 %), surface water (18.6 %) and bank filtrate (1.4 %) (LfS, 2020). The main water users are households and small business (81.9 %). Whereas 18.1 % of the water is used by industry and others. (LfS, 2020).
Onze methodologie omvat het identificeren van de succesfactoren van watergovernanceschema's en het monitoren van hun impact op sociaaleconomische en ecologische welvaart. We zullen ook het potentieel evalueren voor het opschalen van succesvolle oplossingen voor waterbeheer, waaronder bestuurspraktijken, beleidsinstrumenten en prijsbeleid.
Onze lokale activiteiten
Belanghebbenden betrekken bij de aanpak van watergerelateerde problemen
Nieuw beleidsdocument: Wegen naar verbeterd geïntegreerd waterbeheer in het stroomgebied van de bovenloop van de Main
Integrated Water Governance in the Upper Main River Basin The Upper Main River Basin in northern Bavaria confronts mounting climate-related…
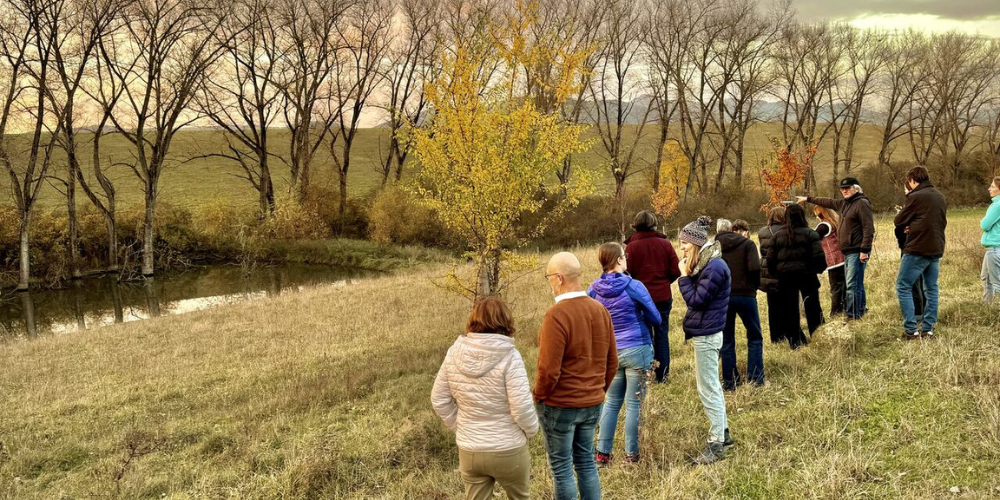
🌿 Nature-Based Solutions in Action: Local Engagement for Water Resilience in Kulmbach and Leuchau
On 18–19 June 2025, our German Case Study hosted two workshops in the Upper Main region (Germany) to promote, validate,…
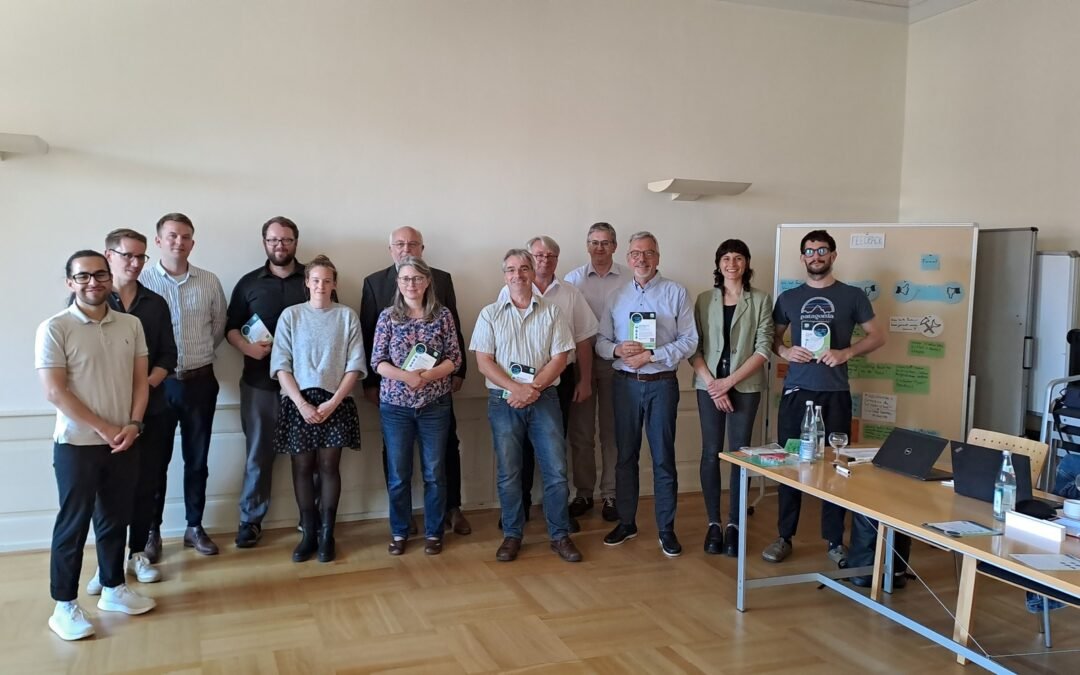
Dialogforum Wasserkontroversen IV: Water Retention in the Landscape – Feasibility, Ecological Benefits, and Legal Implications
The "Wasserkontroversen" dialog forum, a key event in the ongoing discussion of water-related issues, took place on November 8, 2024,…
RETOUCH NEXUS at the Slovak Water Tour 2024: Advancing Nature-Based Solutions for Resilient Water Management
From October 28 to 31, 2024, the Slovak Water Tour brought together experts from across Europe to explore the regeneration…
RETOUCH NEXUS German Case Study at the SWAT Conference: Pioneering WEFE-Based Modeling for Resilient Water Governance in the Upper Main Catchment
From July 8th to 12th, 2024, the RETOUCH NEXUS project proudly participated in the SWAT Conference held at the National…
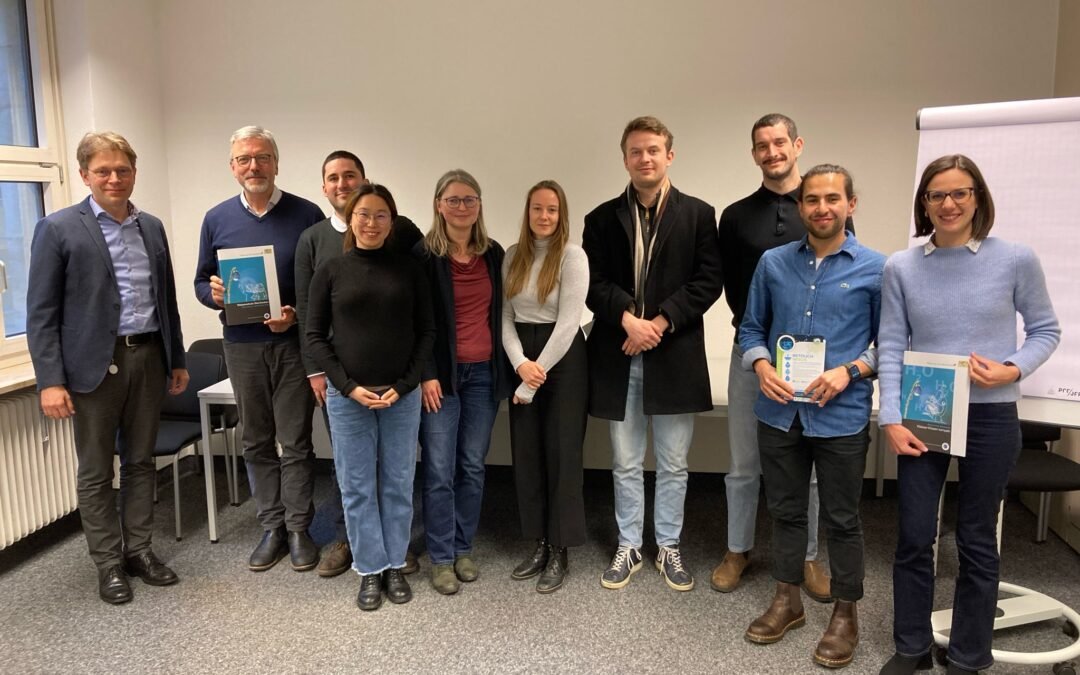
The German case study of the RETOUCH NEXUS project held its First stakeholder engagement in Upper Main!
On 25 June 2024, the German case study of the RETOUCH NEXUS project hosted its first stakeholder engagement workshop in…
RETOUCH NEXUS project coordinator (TUM) visits German Case Study in Bayreuth
On 22 February 2024, a delegation from TUM visited representatives from the German Upper Main government. During the meeting, the…
Establishing a baseline to characterise each RETOUCH NEXUS case study
Last September, our project completed two tasks aimed at exploring water governance models, institutional frameworks and economic, financial and commercial…